Flask中,之前是根据手动设置代码:
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)
app.config.from_object('config.DevelopmentConfig')
# app.config.from_object('config.ProductionConfig')决定到底加载dev开发还是production生产的配置:
config.py
class BaseConfig(object): DEBUG = False FLASK_PORT = 32851 FLASK_HOST = "0.0.0.0" ... class DevelopmentConfig(BaseConfig): DEBUG = True # for local dev, need access remote mongodb MONGODB_HOST = "47.x.x.x" FILE_URL_HOST = "127.0.0.1" class ProductionConfig(BaseConfig): FILE_URL_HOST = "47.x.x.x"
但是每次发布后,都要手动改代码是
config.DevelopmentConfig
还是:
config.ProductionConfig
不够智能。
后来接触到Django中,发现是利用.env
xxx/requirements.txt
python-dotenv==0.7.1
xxx/conf/development/.env
SECRET_KEY = 'xxx' DATABASE_HOST = "localhost" DATABASE_NAME = 'xxx' MONGODB_HOST = 'localhost' MONGODB_PORT = '27017' MONGODB_USERNAME = '' MONGODB_PASSWORD = '' MONGODB_AUTH_SOURCE = ''
/xxx/conf/production/.env
也有自己的配置:
如此,在运行Django的时候,通过:
xxx/wsgi.py
中的:
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "conf.production.settings")加载了production的配置。
而此处,希望:
给Flask中,也去利用,类似于python-dotenv
可以实现:
通过gunicorn的command传入env相关参数
或者是:设置换环境变量
》是dev还是prod
然后代码中,自动检测出当前环境,加载对应配置,无需手动修改代码
flask python-dotenv
抽空去试试
抽空参考上面的帖子去试试
还是:
和
解释的不错
然后才注意到:
xxx/conf/development/settings.py
"""
Django settings for xxx project.
Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 2.0.
For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/settings/
For the full list of settings and their values, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/settings/
"""
import os
# import datetime
from os.path import join, dirname
from dotenv import load_dotenv
dotenv_path = join(dirname(__file__), '.env')
load_dotenv(dotenv_path)
# Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...)
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(
os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
# Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production
# See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/howto/deployment/checklist/
# SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = os.environ.get("SECRET_KEY")
# SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
...就是这么使用的。
去折腾试试
➜ xxxRobotDemoServer git:(master) ✗ pipenv install python-dotenv Courtesy Notice: Pipenv found itself running within a virtual environment, so it will automatically use that environment, instead of creating its own for any project. You can set PIPENV_IGNORE_VIRTUALENVS=1 to force pipenv to ignore that environment and create its own instead. Installing python-dotenv... Looking in indexes: https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple Collecting python-dotenv Downloading https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/packages/24/3d/977140bd94bfb160f98a5c02fdfbb72325130f12a325cf993182956e9d0e/python_dotenv-0.9.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl Installing collected packages: python-dotenv Successfully installed python-dotenv-0.9.1 Adding python-dotenv to Pipfile's [packages]... Pipfile.lock (f83e81) out of date, updating to (81f0dc)... Locking [dev-packages] dependencies... Locking [packages] dependencies... Updated Pipfile.lock (81f0dc)! Installing dependencies from Pipfile.lock (81f0dc)... 🐍 ▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉▉ 34/34 — 00:00:09
然后继续写代码试试
写代码之前,先去搞懂:
【已解决】Python中获取环境变量中os.environ.get和os.getenv的区别
然后再去用代码:
文件结构:
➜ xxxRobotDemoServer git:(master) ✗ tree -L 3 . . ├── Pipfile ├── Pipfile.lock ├── README.md ... ├── app.py ├── conf │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── development │ │ └── __init__.py │ ├── production │ │ └── __init__.py │ └── settings.py ...
其中文件:
conf/development/.env
DEBUG = True # for local dev, need access remote mongodb MONGODB_HOST = "xxx" FILE_URL_HOST = "127.0.0.1"
conf/production/.env
DEBUG = False # for production server, need access server itself mongo, so is localhost MONGODB_HOST = "localhost" FILE_URL_HOST = "xxx"
conf/settings.py
import os
from os.path import join, dirname
from dotenv import load_dotenv
################################################################################
# Common Settings
################################################################################
DEBUG = False
FLASK_PORT = 32851
# FLASK_HOST = "127.0.0.1"
# FLASK_HOST = "localhost"
# Note:
# 1. to allow external access this server
# 2. make sure here gunicorn parameter "bind" is same with here !!!
FLASK_HOST = "0.0.0.0"
# default to production sever's local mongodb
MONGODB_HOST = "localhost"
...
# for periodical celery task
CELERY_TIMEZONE = "Asia/Shanghai"
CELERY_ENABLE_UTC = True
CELERY_REFRESH_MS_TOKEN_INTERVAL = 60 * 9 # 9 minutes (< 10 minutes)
# for debug
# CELERY_REFRESH_MS_TOKEN_INTERVAL = 30
################################################################################
# Load .env for development/production mode
################################################################################
print("Before load .env: DEBUG=%s, MONGODB_HOST=%s, FILE_URL_HOST=%s" %
(DEBUG, MONGODB_HOST, FILE_URL_HOST))
# FLASK_ENV_DEFAULT = "production"
FLASK_ENV_DEFAULT = "development"
cur_flask_environ = os.getenv("FLASK_ENV")
print("cur_flask_environ=%s" % cur_flask_environ)
cur_dir = dirname(__file__)
print("cur_dir=%s" % cur_dir)
env_folder = FLASK_ENV_DEFAULT
if cur_flask_environ:
env_folder = cur_flask_environ
print("env_folder=%s" % env_folder)
dotenv_path = os.path.join(cur_dir, env_folder, '.env')
print("dotenv_path=%s" % dotenv_path)
dotenv_load_ok = load_dotenv(dotenv_path)
print("dotenv_load_ok=%s" % dotenv_load_ok)
DEBUG = os.getenv("DEBUG")
MONGODB_HOST = os.getenv("MONGODB_HOST")
FILE_URL_HOST = os.getenv("FILE_URL_HOST")
print("After load .env: DEBUG=%s, MONGODB_HOST=%s, FILE_URL_HOST=%s" %
(DEBUG, MONGODB_HOST, FILE_URL_HOST))相关的:__init__.py 都是空白
app.py
去调用:
from conf import settings
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)
print("in flask app: settings=%s" % (settings))
# app.config.from_object('config.DevelopmentConfig')
# app.config.from_object('config.ProductionConfig')
# print("for debug: after load from config.DevelopmentConfig: app.config=%s" % (app.config))
app.config.from_object(settings)
print("for debug: after load from settings: app.config=%s" % (app.config))基本上可以输出我们要的效果:
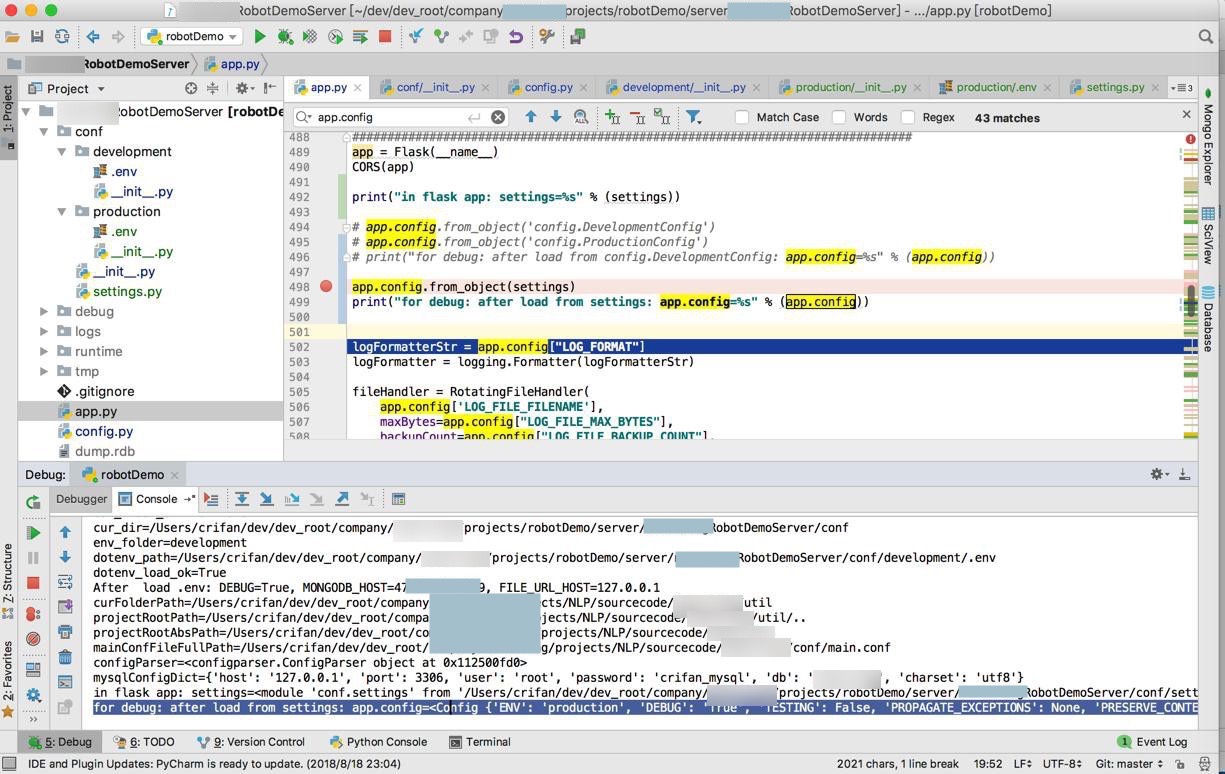
log输出是:
Before load .env: DEBUG=False, MONGODB_HOST=localhost, FILE_URL_HOST=127.0.0.1
cur_flask_environ=None
cur_dir=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/robotDemo/server/xxxRobotDemoServer/conf
env_folder=development
dotenv_path=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/robotDemo/server/xxxRobotDemoServer/conf/development/.env
dotenv_load_ok=True
After load .env: DEBUG=True, MONGODB_HOST=47.x.x.x, FILE_URL_HOST=127.0.0.1
curFolderPath=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/NLP/sourcecode/xxx/util
projectRootPath=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/NLP/sourcecode/xxx/util/..
projectRootAbsPath=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/NLP/sourcecode/xxx
mainConfFileFullPath=/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/NLP/sourcecode/xxx/conf/main.conf
configParser=<configparser.ConfigParser object at 0x112500fd0>
mysqlConfigDict={'host': '127.0.0.1', 'port': 3306, 'user': 'root', 'password': 'crifan_mysql', 'db': 'xxx', 'charset': 'utf8'}
in flask app: settings=<module 'conf.settings' from '/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/company/xxx/projects/robotDemo/server/xxxRobotDemoServer/conf/settings.py'>
for debug: after load from settings: app.config=<Config {'ENV': 'production', 'DEBUG': 'True', 'TESTING': False, 'PROPAGATE_EXCEPTIONS': None, 'PRESERVE_CONTEXT_ON_EXCEPTION': None, 'SECRET_KEY': None, 'PERMANENT_SESSION_LIFETIME': datetime.timedelta(31), 'USE_X_SENDFILE': False, 'SERVER_NAME': None, 'APPLICATION_ROOT': '/', 'SESSION_COOKIE_NAME': 'session', 'SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN': None, 'SESSION_COOKIE_PATH': None, 'SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY': True, 'SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE': False, 'SESSION_COOKIE_SAMESITE': None, 'SESSION_REFRESH_EACH_REQUEST': True, 'MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH': None, 'SEND_FILE_MAX_AGE_DEFAULT': datetime.timedelta(0, 43200), 'TRAP_BAD_REQUEST_ERRORS': None, 'TRAP_HTTP_EXCEPTIONS': False, 'EXPLAIN_TEMPLATE_LOADING': False, 'PREFERRED_URL_SCHEME': 'http', 'JSON_AS_ASCII': True, 'JSON_SORT_KEYS': True, 'JSONIFY_PRETTYPRINT_REGULAR': False, 'JSONIFY_MIMETYPE': 'application/json', 'TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD': None, 'MAX_COOKIE_SIZE': 4093, 'AUDIO_TEMP_FOLDER': 'tmp/audio', 'CELERY_BROKER_URL': '
redis://localhost:6379/0
', 'CELERY_DELETE_TMP_AUDIO_FILE_DELAY': 120, 'CELERY_ENABLE_UTC': True, 'CELERY_REFRESH_MS_TOKEN_INTERVAL': 540, 'CELERY_TIMEZONE': 'Asia/Shanghai', 'FILE_URL_HOST': '127.0.0.1', 'FLASK_APP_NAME': 'RobotQA', 'FLASK_ENV_DEFAULT': 'development', 'FLASK_HOST': '0.0.0.0', 'FLASK_PORT': 32851, 'LOG_FILE_BACKUP_COUNT': 10, 'LOG_FILE_FILENAME': 'logs/RobotQA.log', 'LOG_FILE_MAX_BYTES': 2097152, 'LOG_FORMAT': '[%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(filename)s:%(lineno)d %(funcName)s] %(message)s', 'MONGODB_AUTH_SOURCE': 'gridfs', 'MONGODB_HOST': '47.x.x.x', 'MONGODB_PASSWORD': 'ppwwdd', 'MONGODB_PORT': 23026, 'MONGODB_USERNAME': 'gridfs', 'MS_GET_TOKEN_URL': '
https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken
', 'MS_STT_URL': '
https://westus.stt.speech.microsoft.com/speech/recognition/conversation/cognitiveservices/v1?language=en-US
', 'MS_TTS_SECRET_KEY': 'dxxxf', 'MS_TTS_URL': '
https://westus.tts.speech.microsoft.com/cognitiveservices/v1
'}>加载配置后,关于如何引用,使用这些环境变量,和之前类似可以用app.config[“xxx”]或settings.xxx
print("for debug: output some config value:")
print("settings.DEBUG=%s, settings.MONGODB_HOST=%s, settings.FILE_URL_HOST=%s" %
(settings.DEBUG, settings.MONGODB_HOST, settings.FILE_URL_HOST))
print('app.config["DEBUG"]=%s, app.config["MONGODB_HOST"]=%s, app.config["FILE_URL_HOST"]=%s' %
(app.config["DEBUG"], app.config["MONGODB_HOST"], app.config["FILE_URL_HOST"]))输出:
for debug: output some config value: settings.DEBUG=True, settings.MONGODB_HOST=xxx, settings.FILE_URL_HOST=127.0.0.1 app.config["DEBUG"]=True, app.config["MONGODB_HOST"]=xxx, app.config["FILE_URL_HOST"]=127.0.0.1
另外,也想起来了:
对于从settings中获取配置的话,有个好处:
支持额外设置字典类型参数,比如:
conf/app/settings.py
DEMO_USER = {
"name": "crifan",
"password": "crifan_pwd"
}然后调用:
app.config.from_object(settings)
print('settings.DEMO_USER=%s, settings.DEMO_USER["name"]=' % settings.DEMO_USER, settings.DEMO_USER["name"])输出:
settings.DEMO_USER={'name': 'crifan', 'password': 'crifan_pwd'}, settings.DEMO_USER["name"]= crifan【已解决】Flask中从.env中加载ini类型的配置得到的变量类型不是原始类型而都是字符串
然后接着再去尝试:
在PyCharm中调试时,在命令行中传入FLASK_ENV对应的值,分别是development和production,看看能否正常记载对应的.env的配置:
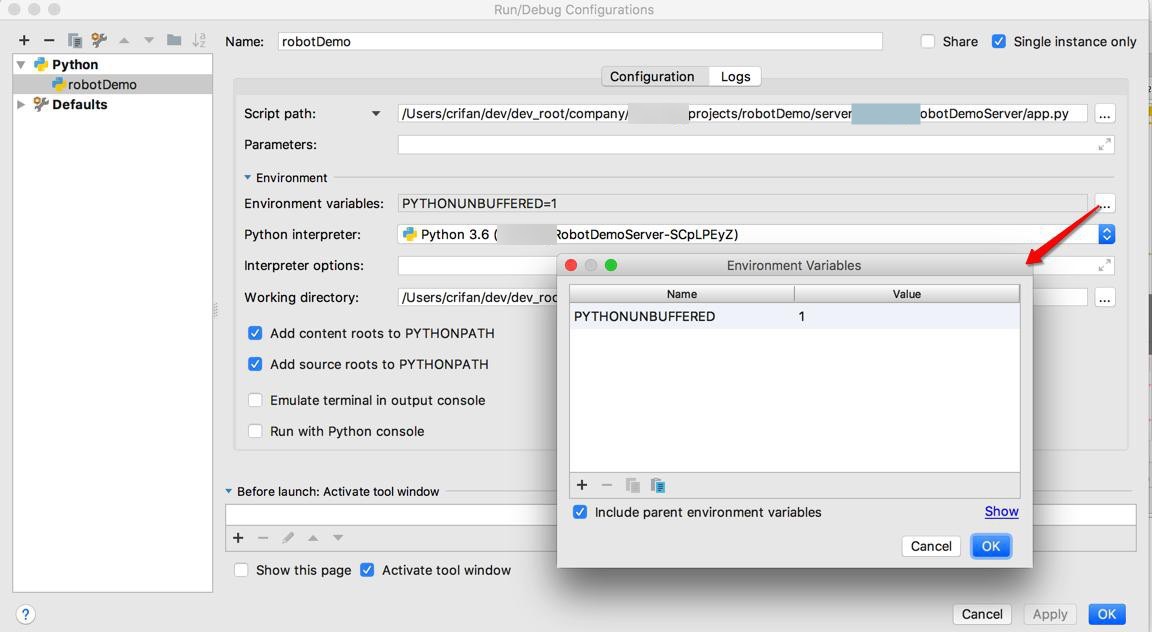
Run-Edit Configurations ->Environment->Environment variables ->点击… 新增
FLASK_ENV=development
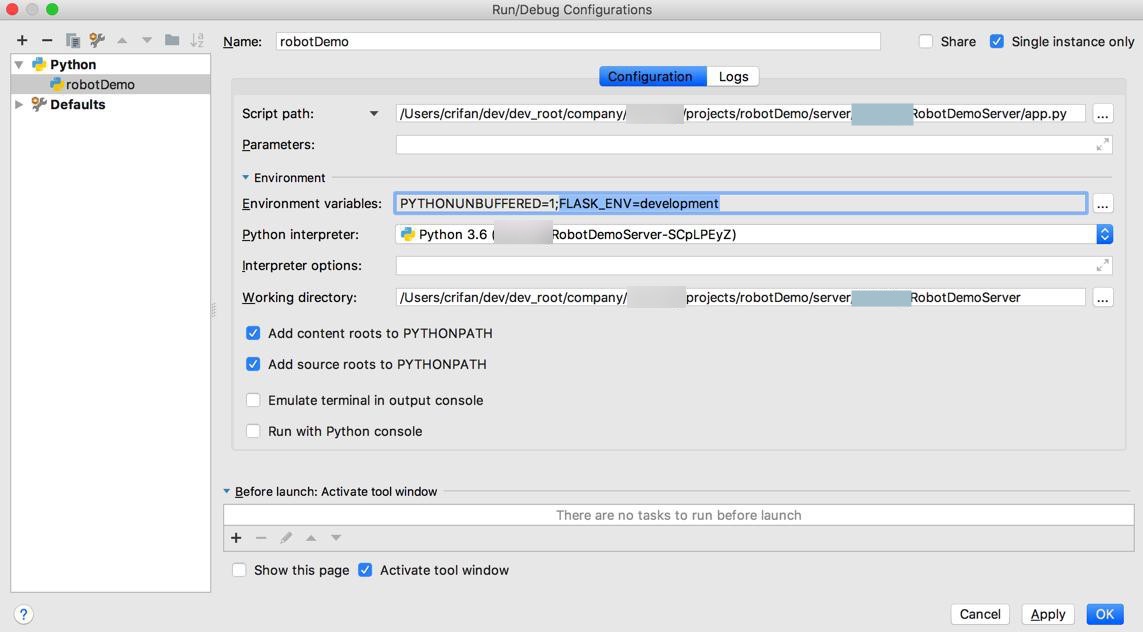
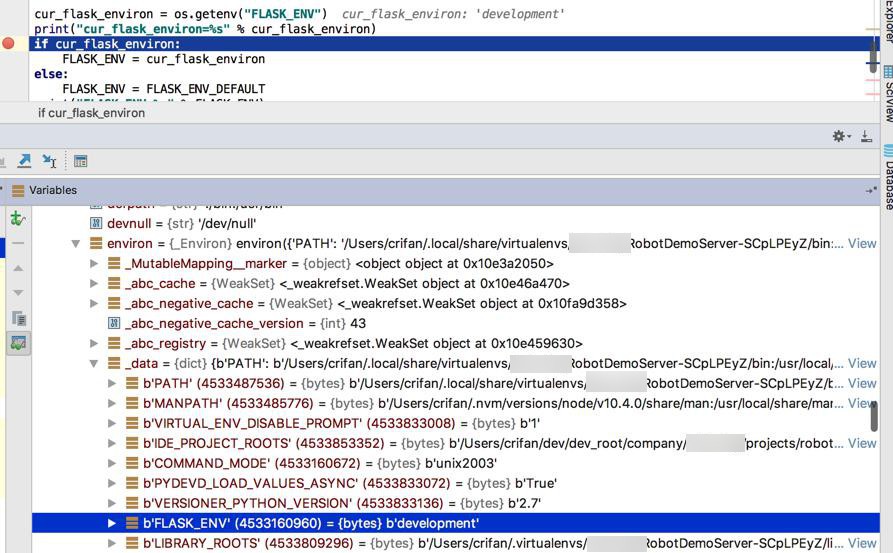
然后再去调试,看看代码中:
cur_flask_environ = os.getenv("FLASK_ENV")能否获取对应的值:
可以的:
然后再改为:
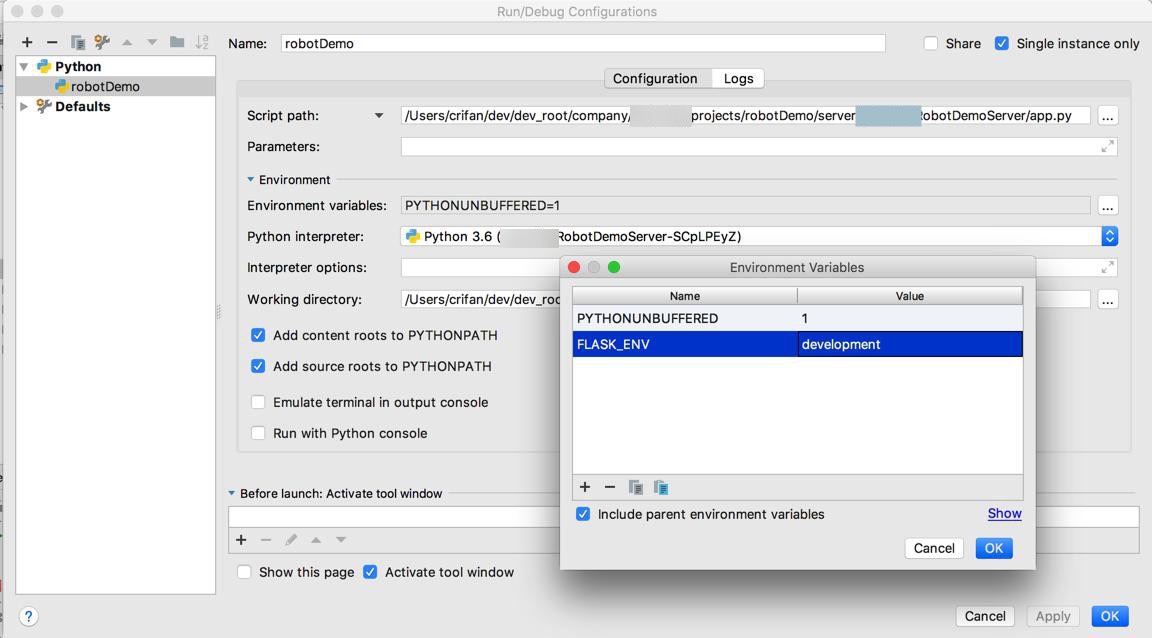
FLASK_ENV=production
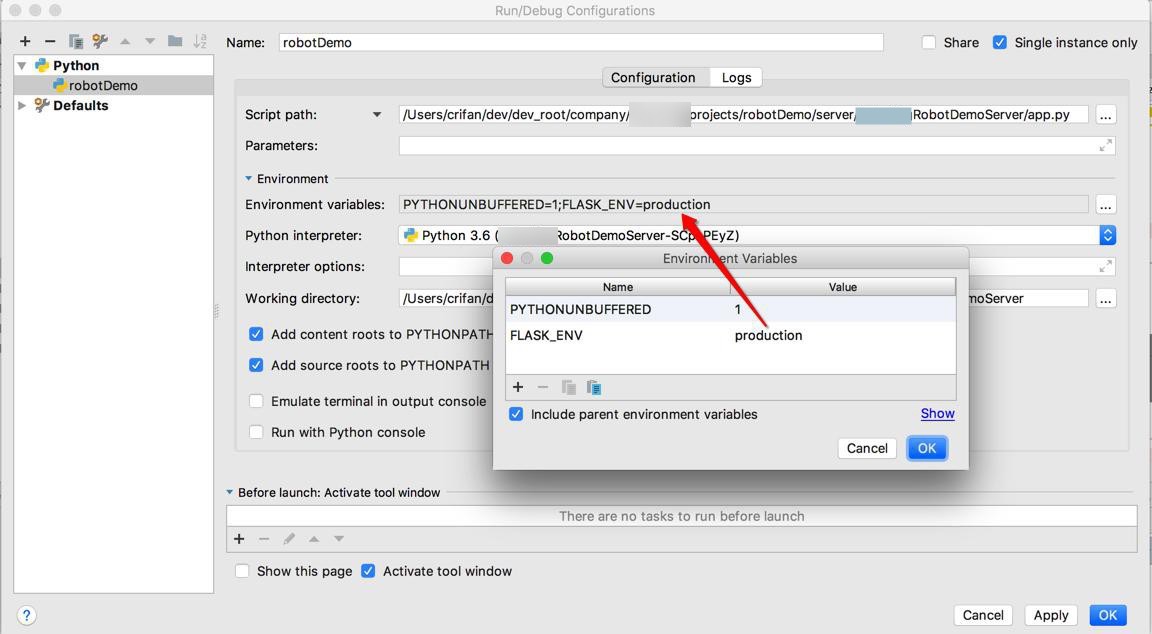
试试,也是可以的:
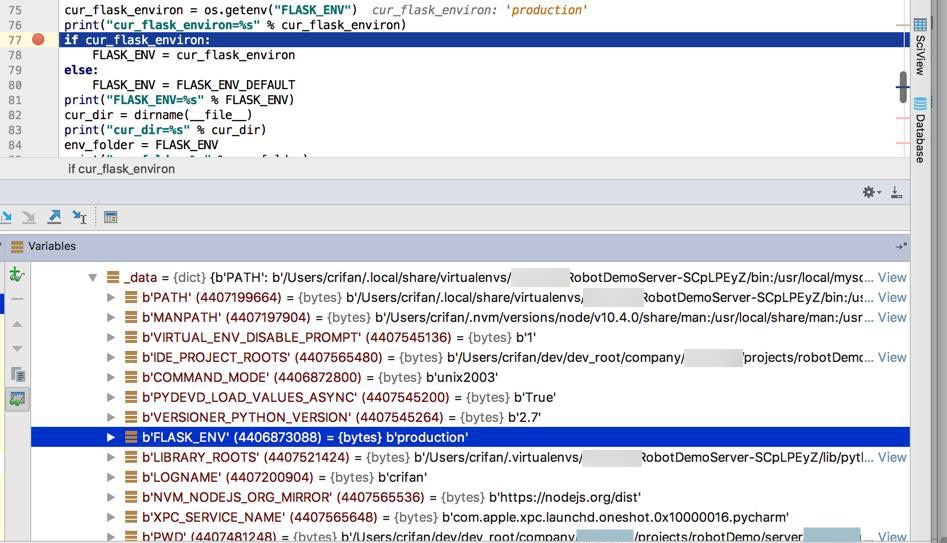
顺带,再去优化配置文件结构,去改为:
➜ xxxRobotDemoServer git:(master) ✗ tree . ... ├── app.py ├── conf │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── app │ │ ├── __init__.py │ │ ├── development │ │ │ └── __init__.py │ │ ├── production │ │ │ └── __init__.py │ │ └── settings.py │ ├── gunicorn │ │ └── gunicorn_config.py │ └── supervisor │ ├── supervisord_local.conf │ └── supervisord_server.conf ...
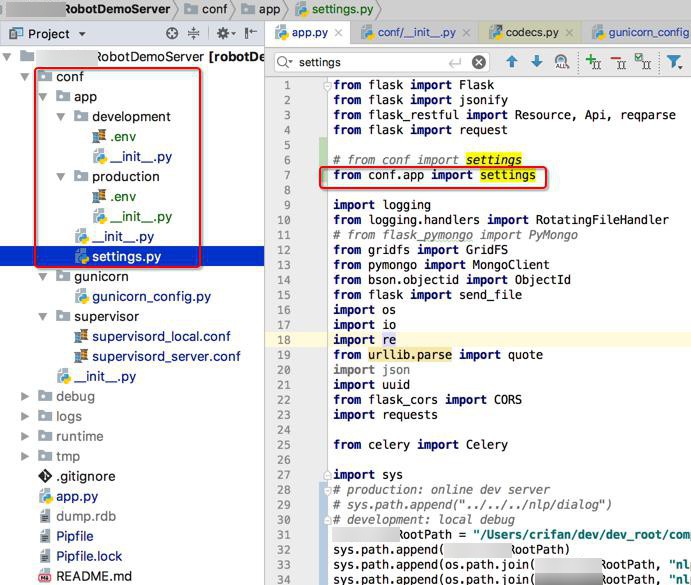
导入方式也变成:
# from conf import settings from conf.app import settings
然后接着要去:
【已解决】Flask本地和线上用gunicorn和supervisor部署时如何传入环境变量
【总结】